What Is a Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet is a form of financial (accounting) report from an organization that discloses the value of its assets, liabilities, and equity as of a certain date. The publication frequency of balance sheet data depends on the frequency of reporting as a whole. As a rule, this happens quarterly, semi-annually, or once a year.
A balance sheet is one of the key forms of reporting a company must perform, along with reporting on financial results (profits and losses), cash flow, and changes in capital.
Balance Sheet in Different Reporting Standards
As a part of reporting prepared in accordance with international standards, the balance sheet of an organization is called a statement of financial position. For instance, below, you will find a report from Emirates Telecom in the UAE as of June 30, 2023.
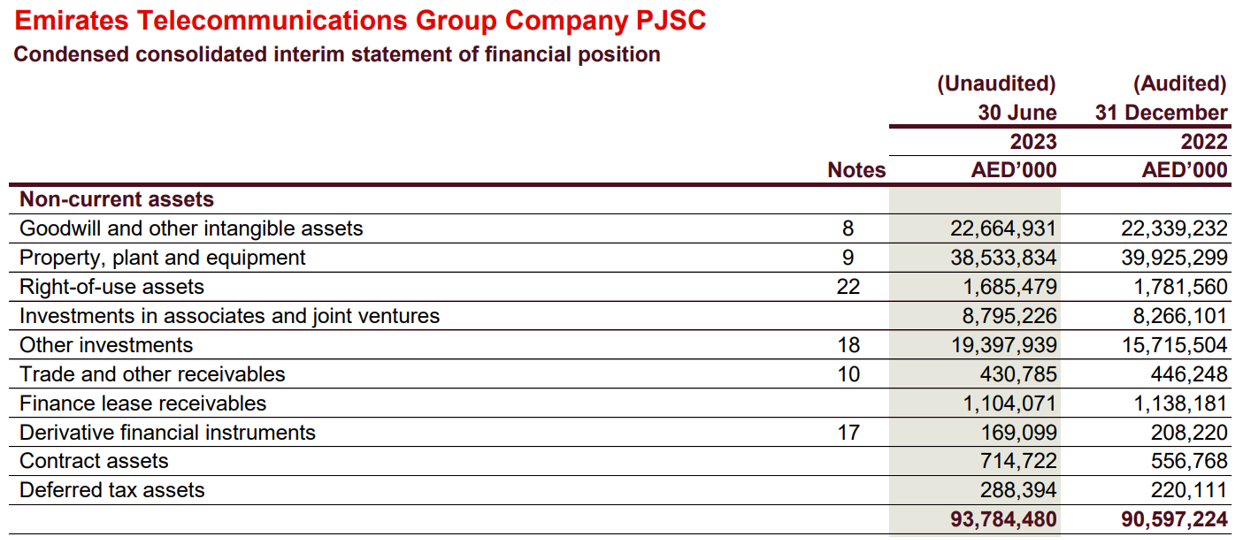
The procedure for financial statement disclosure in IFRS is regulated by the IAS 1 standard, entitled “Presentation of Financial Statements.”
As a part of RAS reporting that is composed and published by Russian companies, this form is called the balance sheet. Below, can view an example from United Heavy Machinery (UHM).

The balance sheet form 0710001 is established by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010, No. 66n, entitled “On Forms of Financial Statements of Organizations”.
As part of reporting based on US GAAP standards, which are mainly applied by US companies, the document is usually called a “balance sheet,” as with, for example, Apple, Microsoft, and Tesla.
The Balance Sheet Structure
In general, regardless of the standards applied to corporate reporting, the balance sheet structure is as follows:
- Assets
● Non-current assets
● Current assets
- Liabilities
● Short-term liabilities
● Long-term liabilities
● Equity
It is worth mentioning that the total volume of the company’s assets must be equal to the total value of its liabilities, that is, the sum of liabilities and sources of equity.
A number of companies, the financial sector in particular (banks, leasing, insurance, investment companies, etc.), do not separate their assets into current and non-current and arrange them in order of decreasing or increasing liquidity.
This is due to the specifics of their activities, since such companies do not supply goods and services during a particular operational cycle. Examples here include issuers such as Al Wathba National Insurance, Sohar International Bank, and Finance House.
Bond Screener
Watchlist
Excel Add-in
API